Deuterated DMSO
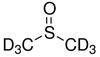
Deuterated DMSO, also known as dimethyl sulfoxide-d6, is an isotopologue of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO, (CH3)2S=O)) with chemical formula ((CD3)2S=O) in which the hydrogen atoms ("H") are replaced with their isotope deuterium ("D"). Deuterated DMSO is a common solvent used in NMR spectroscopy.
Production
Deuterated DMSO is produced by heating DMSO in heavy water (D2O) with a basic catalyst such as calcium oxide. The reaction does not give complete conversion to the d6 product, and the water produced must be removed and replaced with D2O several times to drive the equilibrium to the fully deuterated product.
Use in NMR spectroscopy
Pure deuterated DMSO shows no peaks in 1H NMR spectroscopy
and as a result is commonly used as an NMR solvent. However
commercially available samples are not 100% pure and a residual DMSO-d61H NMR signal is observed at 2.50ppm
(quintet, JHD=1.9Hz). The 13C chemical shift of DMSO-d6 is 39.52ppm (septet)
Ref:

 ناشناس
ناشناس
