NMR solvents are another form (called isotopologue) of organic solvents in which the hydrogen atoms ("H") are replaced with deuterium (heavy hydrogen) isotope ("D"). NMR solvents are common solvent used in NMR spectroscopy.

Isotope Stable:
The atoms of a chemical element can exist in different types. These are called isotopes. They have the same number of protons (and electrons), but different numbers of neutrons. Different isotopes of the same element have different masses. Massis the word for how much substance (or matter) something has. Things with different masses have different weights. Because different isotopes have different numbers of neutrons, they do not all weigh the same or have the same mass.
Different isotopes of the same element have the same atomic number. They have the same number of protons. The atomic number is decided by the number of protons. Isotopes have different mass numbers, though, because they have different numbers of neutrons.
The word isotope, meaning at the same place, comes from the fact that isotopes are at the same place on the periodic table.
In a neutral atom, the number of electrons equals the number of protons. Isotopes of the same element also have the same number of electrons and the electronic structure. Because how an atom acts is decided by its electronic structure, isotopes are almost the same chemically, but different physically to their original atoms.
Heavier isotopes react chemically slower than lighter isotopes of the same element. This "mass effect" is larger for protium (1H) and deuterium (2H), because deuterium has twice the mass of protium. For heavier elements, the relative atomic weight ratio between isotopes is much less, and the mass effect is usually small.
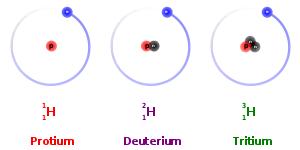
Isotopes are the atoms of the same element that differ in atomic mass, due to difference in the number of neutrons contained in the atom’s nuclei. Isotopes are categorized into two specific types: stable and unstable. For example, the three most abundant isotopes of the Hydrogen are Hydrogen-1 (1H), which contains 1 proton, 1 electron, and 1 neutron; Hydrogen-2 (2H or D), which also has 1 proton and electron, but 2 neutron; and Hydrogen-3 (3H or T) which also contains 1 proton and 1 electron, but 3 neutrons. Having too few or too many neutrons compared to protons causes some isotopes such as 3H to be unstable. These unstable radioisotopes will decay to stable products.
Other isotopes such as 1H and 2H do not decay, because their particular combinations of neutrons are stable. These kinds of isotopes are known as stable isotopes. The relative abundance of stable isotopes in the same compounds from different sources could be different due to the thermodynamic and kinetic effects during chemical and physical process. It can be measured experimentally (isotope analysis), yielding an isotope ratio that is used as a research tool. As a result, stable isotopes have been founding several applications in variety of research areas including the following fields of science:
ref :

